Ethane
Ethane
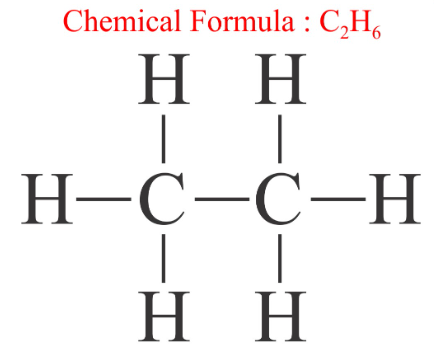
What is Ethane?
Ethane is a saturated hydrocarbon found in gaseous state. Ethane is the second simplest alkane followed by methane. It contains 2 carbon atoms and 6 hydrogen atoms. So the formula for ethane is C2H6. It is prepared by laboratory method using sodium propionate. Ethane is the most important gaseous fuel. Natural gas components of ethane and heavier hydrocarbons are quite easily separated from the gas stream and liquefied under moderate pressure.
Other names – Methyl methane, Bimethyl, Dimethyl, Ethyl hydride
| C2H6 | Ethane |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.36 kg/m³ |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 30.07 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | -89 °C |
| Melting Point | -182.8 °C |
| Chemical Formula | C2H6 |
Synthesis of Ethane – C2H6
Ethane is synthesized by reduction of ethyl iodide using zinc + copper couple in alcohol. The chemical equation is given below.
CH3CH2I + 2[H] → C2H6 + HI
Ethane is also prepared by Wurtz reaction. When methyl bromide or methyl iodide and sodium are heated in the presence of dry ether ethane is formed.
CH3I + 2Na + CH3I → CH3– CH3 + 2NaI
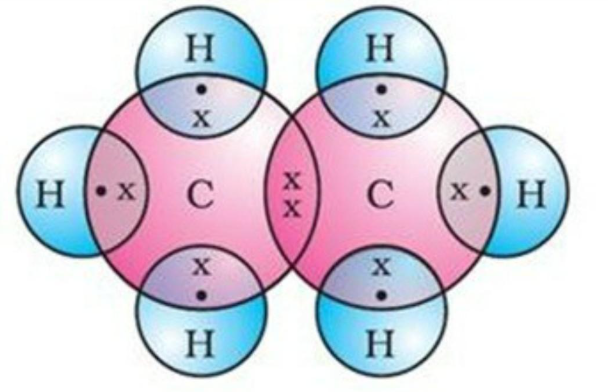
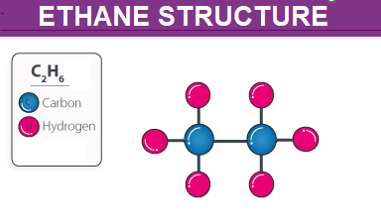
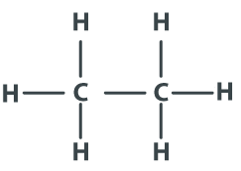
Ethane Structure – C2H6
Physical Properties of Ethane – C2H6
| Odour | Odourless |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Colourless gas |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit | 7 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 2 |
| Nature of compound | Saturated compound |
| Solubility | Soluble in water |
Uses of Ethane – C2H6
- Used in the petrochemical industry as a fraction of that produced in the natural gas liquids plants alone.
- Used in the preparation of ethanol, acetaldehyde and acetic acid which find use in paints, varnishes, adhesive, plastic etc.
- Used as the most specific volatile marker for the investigation of lipid peroxidation.
- Used to make ethylene, for everything from antifreeze to plastics to ripening fruit.
