Ethylene
Ethylene
What is Ethylene C2H4?
Ethylene is a group of plant growth regulators which are widely used for ripening fruits and for the production of more flowers and fruits.
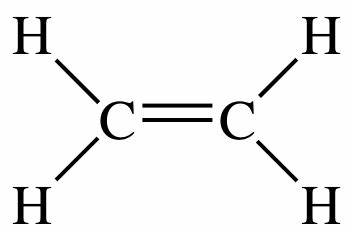
Ethylene is a small hydrocarbon, the colorless flammable gas which is denoted by a formula C2H4 or H2C=CH2. Ethene is the IUPAC name for ethylene. It has a “sweet and musky” odor when it is pure. It is the simplest alkene and also the second simplest unsaturated hydrocarbon C2H2.
Ethylene is abundantly used in the chemical industry, and the polyethene is extremely produced using ethylene. Further, ethylene is also used in agricultural practices to ripen fruits, germination of the seed, etc.
Ethylene is a group of plant growth regulators which are widely used for ripening fruits and for the production of more flowers and fruits.
Ethylene is a small hydrocarbon, the colourless flammable gas which is denoted by a formula C2H4 or H2C=CH2. Ethene is the IUPAC name for ethylene. It has a “sweet and musky” odour when it is pure. It is the simplest alkene and also the second simplest unsaturated hydrocarbon C2H2.
Ethylene is abundantly used in the chemical industry, and the polyethene is extremely produced using ethylene. Further, ethylene is also used in agricultural practices to ripen fruits, germination of the seed, etc.
Let us have a look at the ethene structure and formula.
What is Ethylene C2 H4 ?
| C2 H4 | Ethylene |
| Molecular weight of C2 H4 | 28.054 g/mol |
| Density of Ethylene | 1.178 kg/m3 |
| Boiling point of Ethylene | −103.7 °C |
| Melting point of Ethylene | −169.2 °C |
C2H4 + 3O2 ⟶ 2CO2 + 2H2 O
n[CH2 =CH2 ] ⟶ [ーCH2 ーCH2 ー] n
Ethylene Structure
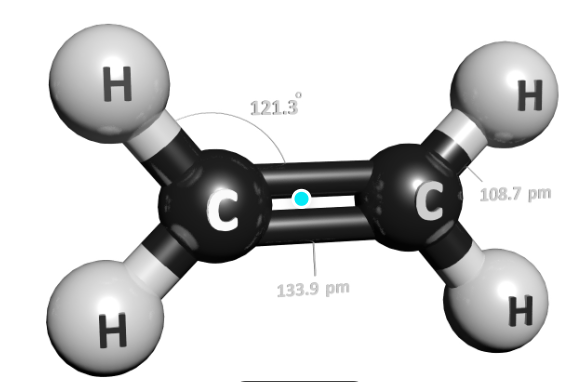
Ethylene is a hydrocarbon. As the name suggests it has four atoms of hydrogen bonds that are paired with carbon atoms with a double bond. All these six atoms H-C-H form an angle of 117.4°, close to the 120° to form a hybridized carbon sp². Further, the bond is rigid about the C-C bond with high energy process by breaking the π-bond.

Ethylene Formula
The ethylene formula is written as:
C2H4
or
H2C=CH2
Also Read: cytokinins
Ethylene as a Plant Hormone
The ethylene in a plant growth regulator that acts as a trace level of entire plant life by regulating and stimulating the opening of flowers, fruit ripening and shedding of leaves.
During the ancient days, Egyptians used this technique with gash figs to stimulate ripening. While the Chinese burn incense in a closed room to fasten the ripening of pears. This plant hormone is essentially produced in all parts of grown plants including roots, stems, tubers, leaves, flower, fruits and seeds.
Ethylene is the most widely used plant growth regulator as it plays a vital role in:
- Stimulating fruit ripening.
- Helps in determining the sex of a flower.
- It is involved in the production of female flowers in a male plant.
- Promotes Apo-geotropism in roots.
- Helps in the root initiation and pollination.
- Ethylene increases the speed of leaf and flower senescence.
- Induces seed germination.
- Induces root growth to increase the capability of water and mineral absorption.
- Stimulates epinasty.
- Induces a climacteric rise in respiration in some fruits.
- Effects gravitropism.
- Stimulates nutational bending.
- Inhibits stem growth.
- Interference with auxin transport.
- Induces flowering in pineapples.
Also Read: Gibberellins
Ethylene Function
Following are the important function of ethylene:
Growth
Ethylene stimulates horizontal growth and the swelling of the axis. It inhibits the growth in the longitudinal direction.
Gravity
It reduces the sensitivity to gravity. The stems become positively geotropic and the leaves and flowers undergo drooping.
Senescence
It speeds up the senescence of flowers and leaves.
Abscission
Ethylene stimulates the abscission of flowers, leaves, fruits and other parts of the plant. It helps in the formation of hydrolases.
Apical Dominance
It prolongs dormancy of lateral buds and promotes apical dominance.
Breaking Dormancy
It breaks the dormancy of seeds, buds and storage organs
Ripening of Fruit
Ethylene induces artificial ripening of climacteric fruits such as banana, mango, apple, etc.
Flowering
Ethylene induces flowering in plants like pineapple and mango. In some plants, it also causes fading of flowers.
Uses Of Ethylene
Following are some of the important uses of ethylene:
- It regulates a number of physiological processes and hence is used as a plant growth regulator.
- Ethylene lamps are used for colour development and ripening of fruits such as banana, mango, apple, etc.
- It induces a feminising effect in plants, i.e., it is used to increase the number of female flowers in a plant to induce fruiting.
- It is applied to rhizomes, tubers and seeds to induce early sprouting in them.
- It is used for thinning of excess flowers and young fruits such as walnuts, cherry, cotton, etc.
