Methane
Methane
What is Methane?
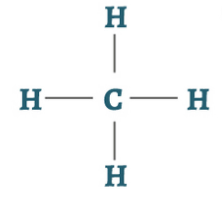
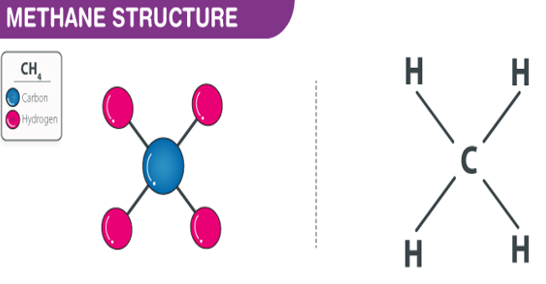
Methane is the simplest of saturated hydrocarbons with a chemical formula CH4. It consists of four hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom and is the simplest alkane.
When natural methane reaches the surface of the atmosphere is called atmospheric methane and can be found under the seafloor as well as below the ground.
It is odorless or has a sweet oil type smell and has no color. It is a flammable non-toxic gas. It is a tetrahedral molecule which has four equivalent C-H bonds. It is produced by colonic anaerobes. Alessandro Volta an Italian physicist was the first to scientifically identify methane in the year 1776.
Properties of Methane – CH4
Methane is one of the most important greenhouse gas and approximately 70% of methane emissions are linked to human activities. Pure methane is an energy-rich feedstock with an energy density of 55.7 MJ/kg and is used to generate electricity, for domestic heating and cooking
| CH4 | Methane |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 16.04 g/mol |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 146.06 g/mol |
| Density | 0.656 kg/m³ |
| Boiling Point | −161.50 °C |
| Melting Point | −182.5 °C |
Methane Structure – CH4
CH4 Uses (Methane)
- It is used in automobiles, ovens and water heaters as fuel.
- It is used in the generation of electricity
- It is used as rocket fuel in its refined liquid form
- It is used as an antifreeze ingredient in industries
- It is a common ingredient in fertilizer
- It is used to sanitize products
- It is used to sanitize products
- It is used in gas cookers
- It is used in the testing of gas appliances
Tetracyano methane
Tetracyano methane or carbon tetra cyanide is a peranakan molecular carbon nitride with formula C(CN)4. The structure can be considered as methane with all hydrogen atoms replaced by cyanide groups.
Tetracyano methane, C(CN)4, is a tetrahedral molecule containing a central sp3 carbon that is coordinated by reactive nitrile groups that could potentially transform to an extended CN network with a significant fraction of sp3 carbon. High-purity C(CN)4 was synthesized, and its physiochemical behavior was studied using in situ synchrotron angle-dispersive powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and Raman and infrared (IR) spectroscopies
